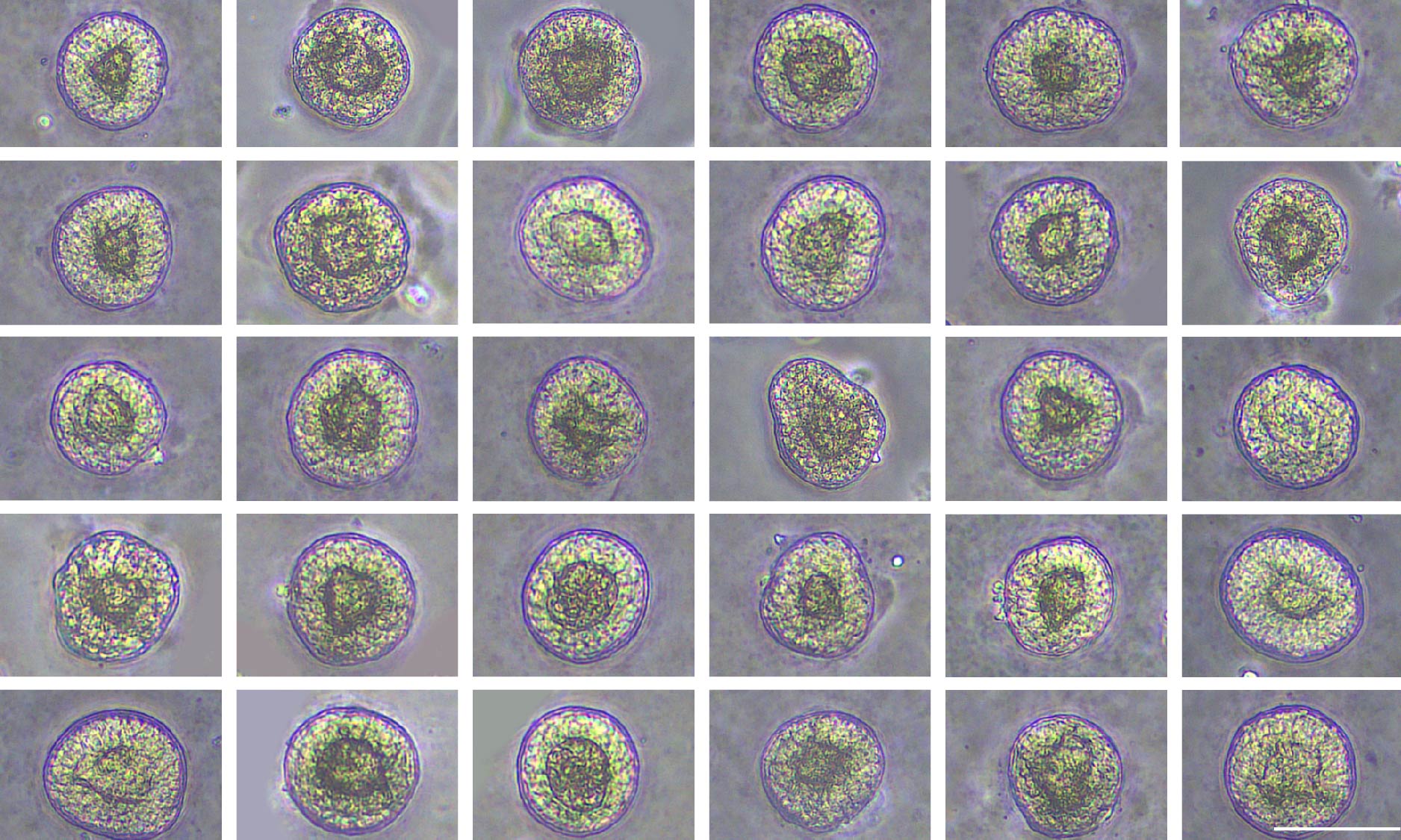
“即用型iPSC源肝类器官 (s-model)”是以人诱导多能干细胞(iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cells)为起点细胞,基于肝脏发育进程的关键分子信号,凭借iPSC谱系共分化技术诱导分化形成。iLiver具有更接近人真实肝脏的细胞谱系及结构特征,为肝脏发育机制的探索、肝病模拟、药物开发与评价等研究提供可靠的模型工具。
| 遗传信息 | |||
| • 类器官类型: | • 来源: | • 性别: | |
| 肝类器官 | 成纤维细胞 | 女 | |
| • 捐助者状态: | • 年龄: | ||
| 健康 | 20 |
Characteristics
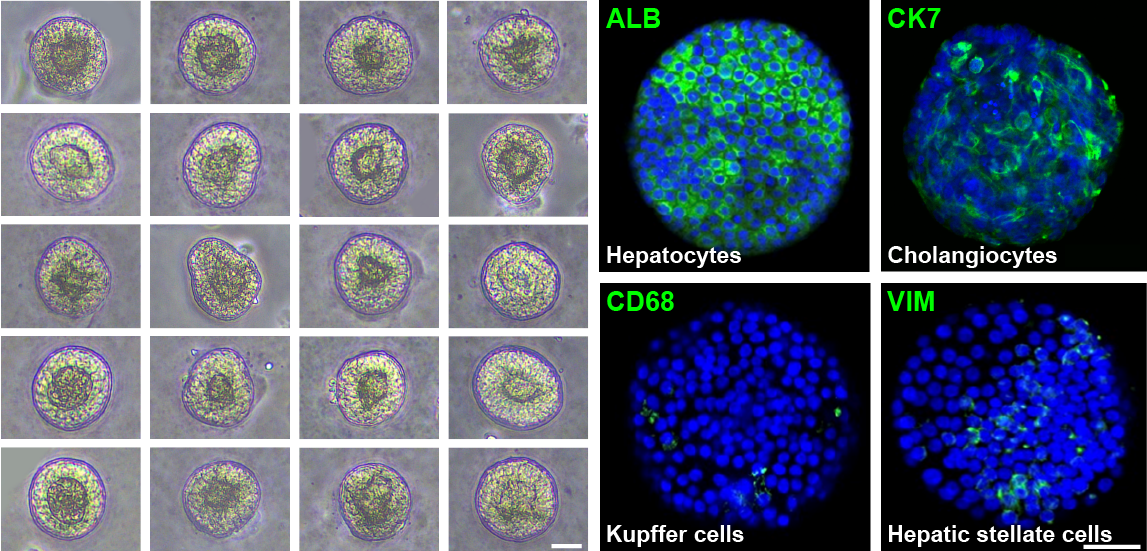
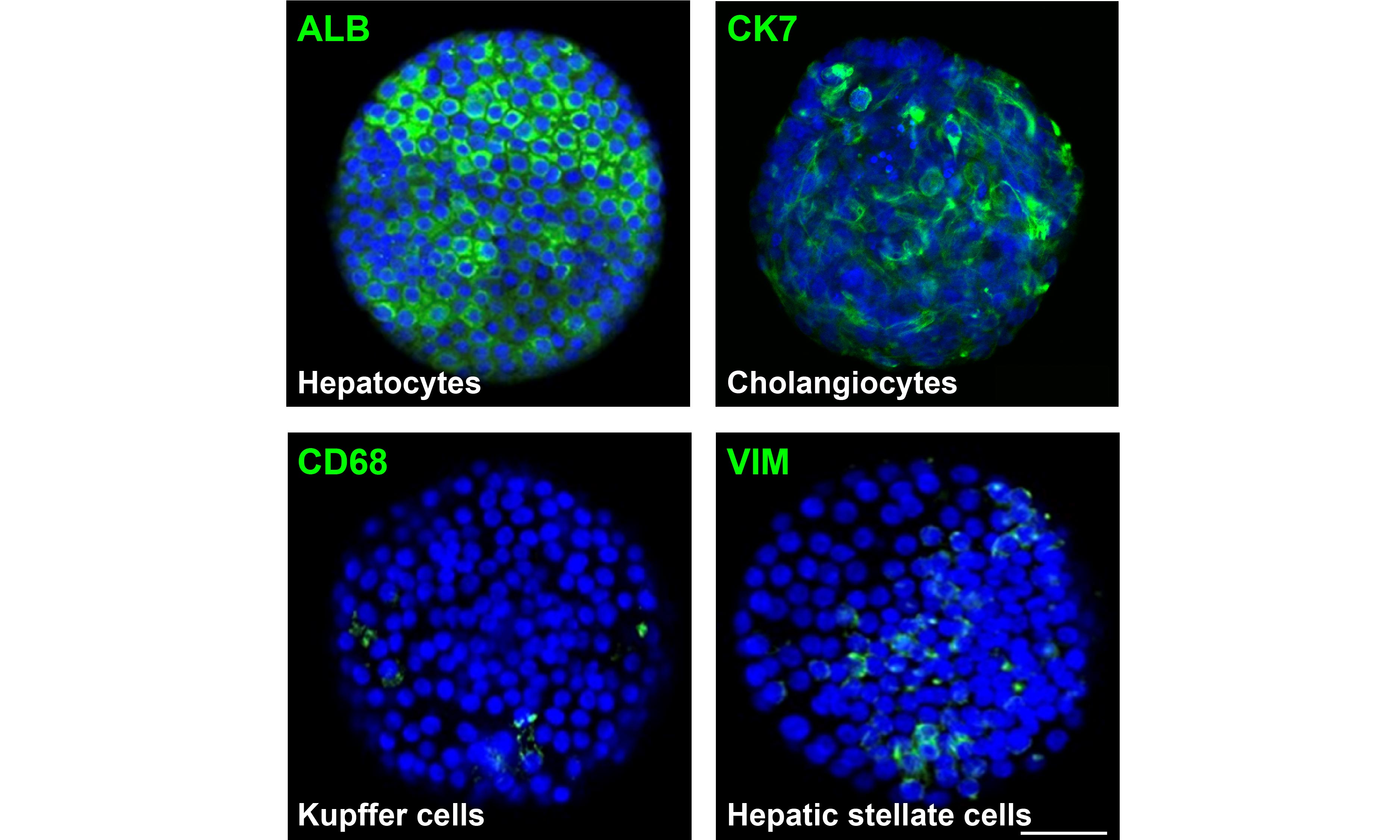
Day-25 iLivers represent uniformly sized 3D spheroids, which consists of hepatocytes (ALB+), cholangiocytes (CK7+), Kupffer cells (CD68+) and hepatic stellate cells (VIM+), as identified by immunofluorescence. Scale bar = 50 μm.
Application of iLiver Organoids
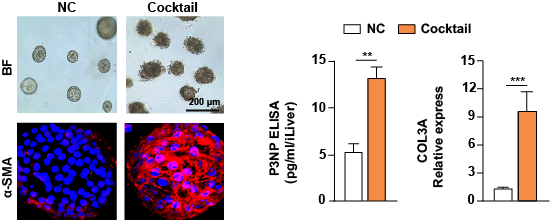
Modeling MASH using day-24 iLivers manifested excessive accumulation of fibrosis (a-SMA staining), along with an increased secretion level of clinical fibrosis marker PIIINP by ELISA analysis.
Drug Metabolism in iLivers

Liu F, Liu T, Wu X, et al. iPSC-induced multilineage liver organoids, small intestinal organoids and brain organoids sustain pangenotype hepatitis E virus propagation[J]. Gut, 2025.
Tadokoro T, Murata S, Kato M, et al. Human iPSC–liver organoid transplantation reduces fibrosis through immunomodulation[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2024, 16(757): eadg0338.
Zhang C J, Meyer S R, O’Meara M J, et al. A human liver organoid screening platform for DILI risk prediction[J]. Journal of hepatology, 2023, 78(5): 998-1006.
Guan Y, Enejder A, Wang M, et al. A human multi-lineage hepatic organoid model for liver fibrosis[J]. Nature communications, 2021, 12(1): 6138.
Wu D, Chen X, Sheng Q, et al. Production of functional hepatobiliary organoids from human pluripotent stem cells[J]. International journal of stem cells, 2021, 14(1): 119-126.
Wu F, Wu D, Ren Y, et al. Generation of hepatobiliary organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Journal of Hepatology, 2019, 70(6): 1145-1158.