使用“iPSC向肺类器官分化试剂盒 (Cat. 3d0010) ”诱导分化产生
呈现出多级分叉结构与早期肺泡样结构,其中至少包含了肺泡I-II型细胞、基底细胞、棒状细胞、纤毛细胞、肺神经内分泌细胞、巨噬细胞、间充质细胞、成纤维细胞等肺泡及气道生理相关的谱系类型
经过肺纤维化、病毒感染、细菌感染等验证
该模型是研究肺脏发育、呼吸疾病及药物筛选的精准人源化工具
“即用型iPSC源肺类器官(s-model)”呈现出多级分叉结构与早期肺泡样结构,其中至少包含了肺泡I-II型细胞、基底细胞、棒状细胞、 纤毛细胞、肺神经内分泌细胞、巨噬细胞、间充质细胞、成纤维细胞等肺泡及气道生理相关的谱系类型。支持肺脏发育机制的探索、呼吸道疾病的模拟与病理解析、药物开发、以及体内定植等研究。
| 遗传信息 | |||
| • 类器官类型: | • 来源: | • 性别: | |
| 肺类器官 | 成纤维细胞 | 女 | |
| • 捐助者状态: | • 年龄: | ||
| 健康 | 20 |
Characteristics
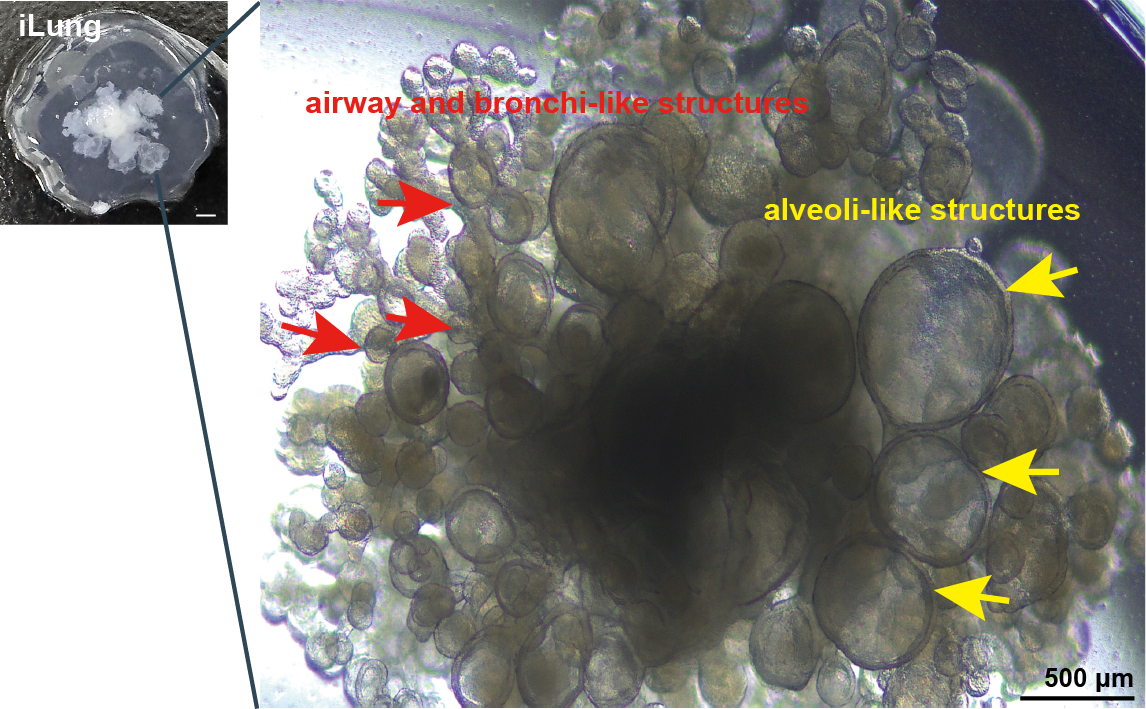
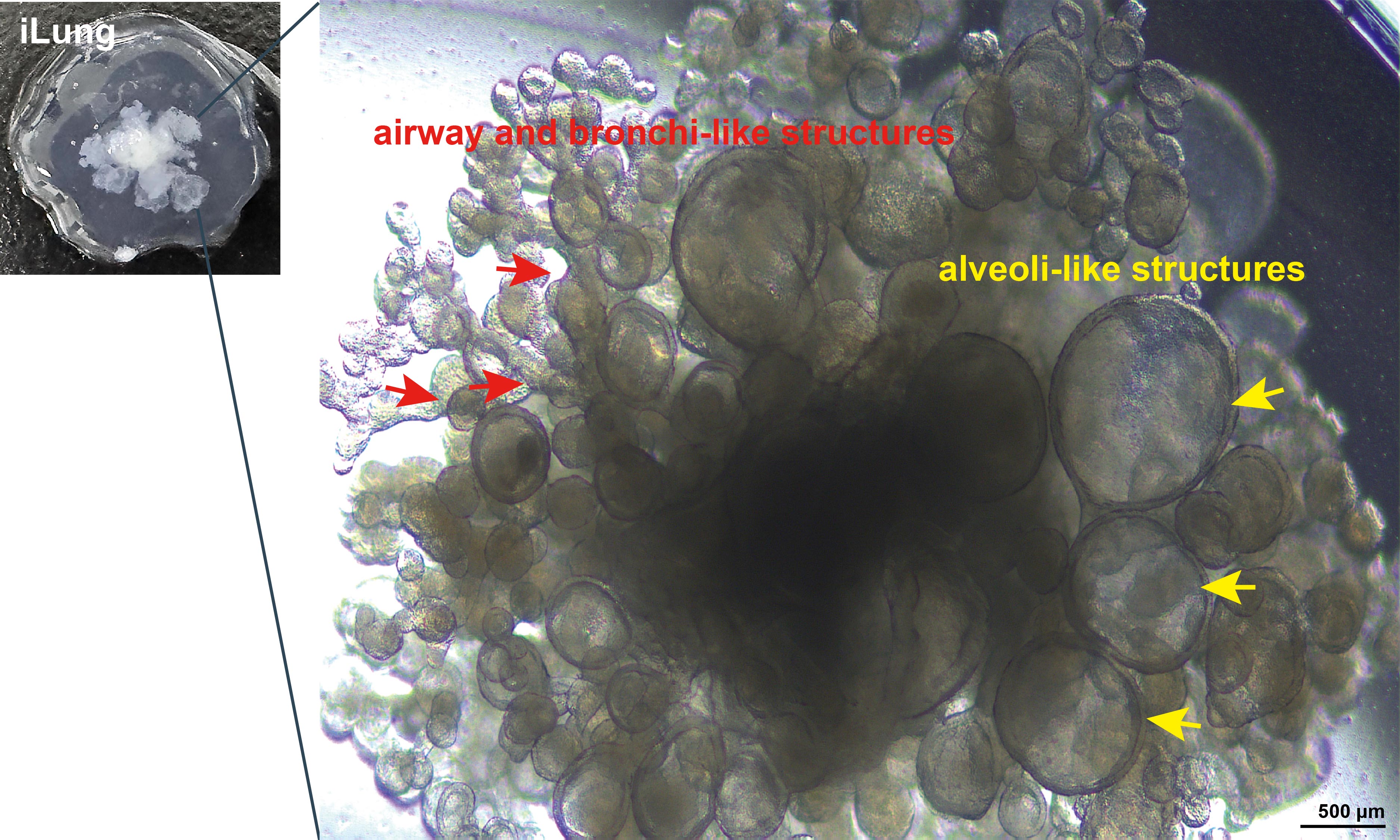
A day-55 iLung organoids presented airway-like and bronchi-like structure, alveoli-like structures. Scale bar = 500 μm.
Characteristics
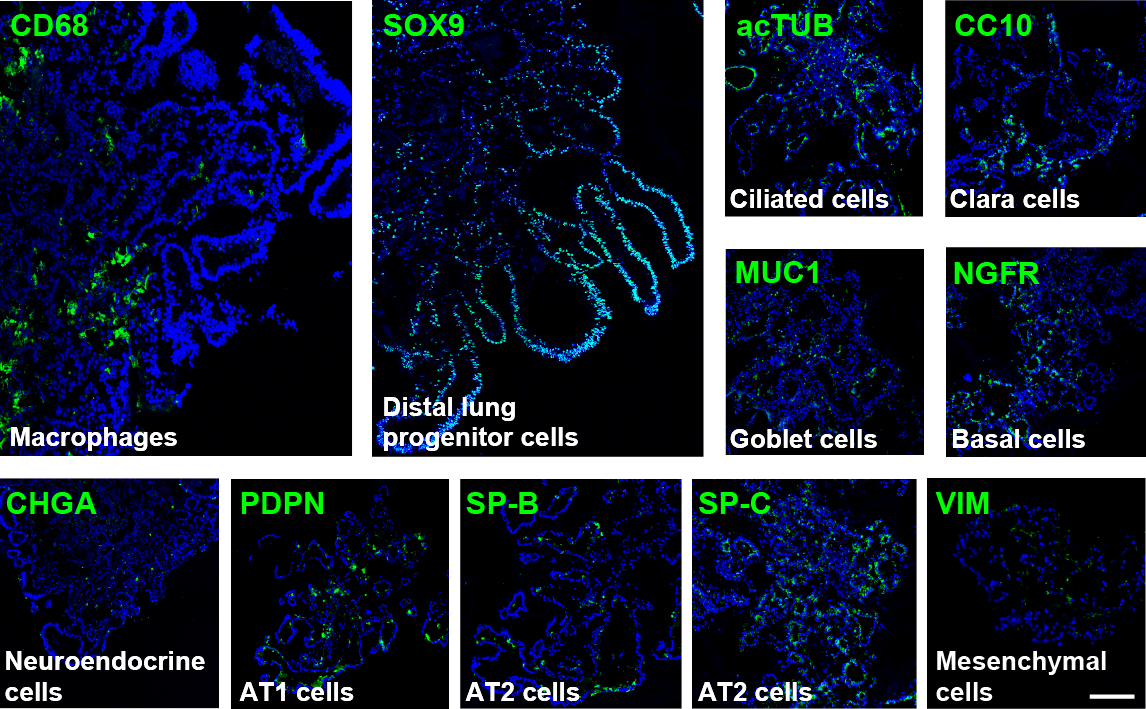
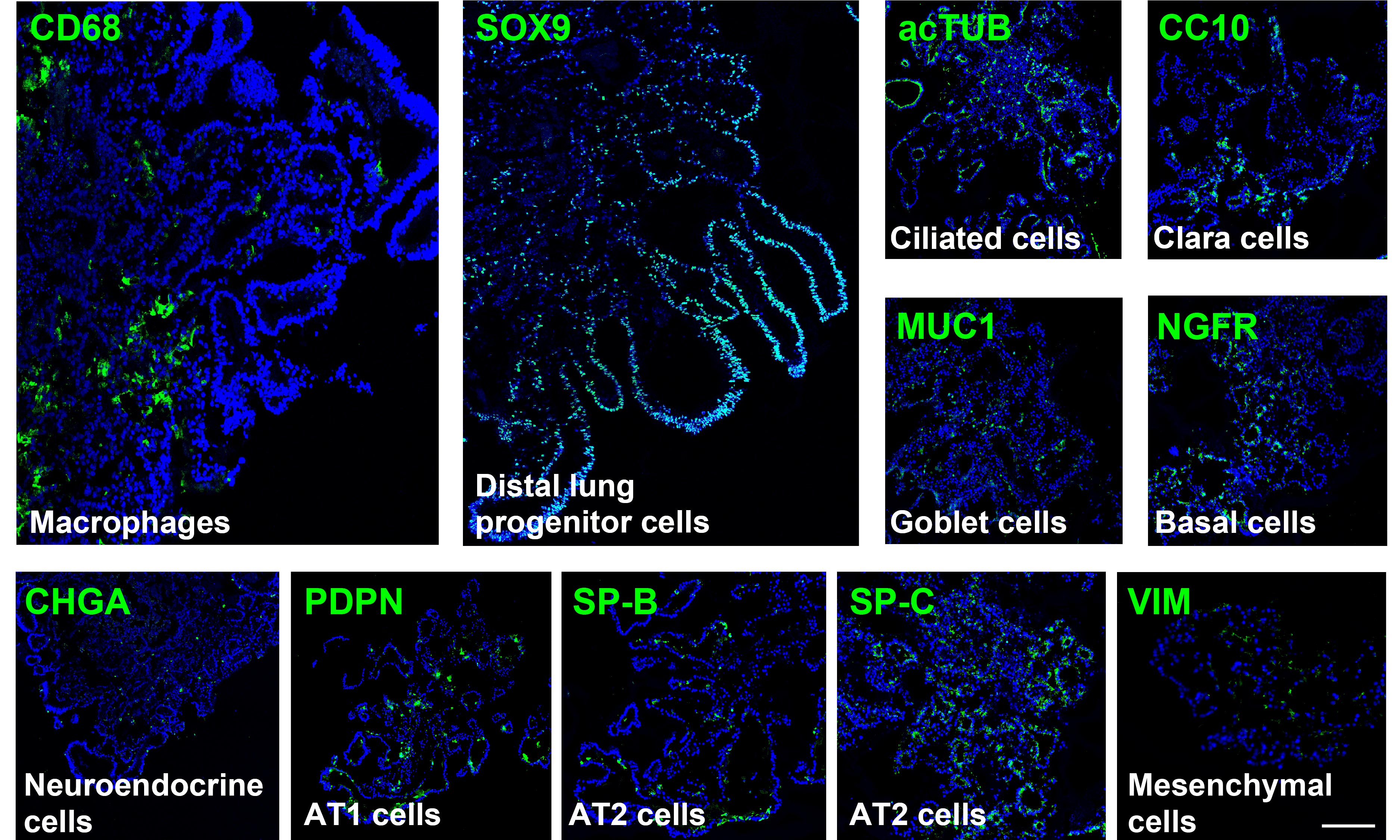
Immunofluorescence staining of a day-60 iLung demonstrated the presence of both proximal airway and distal alveolar cell types, including ciliated cells (AcTUB+), basal cells (NGFR+), club cells (CC+), goblet cell (MUC1+), neuroendocrine cells (CHGA+), type I cells (PDPN+), type II cells (SP-B+, SP-C+), resident macrophages (CD68+) and fibroblasts (VIM+). Scale bar = 200 μm.
Application of iLung Organoids
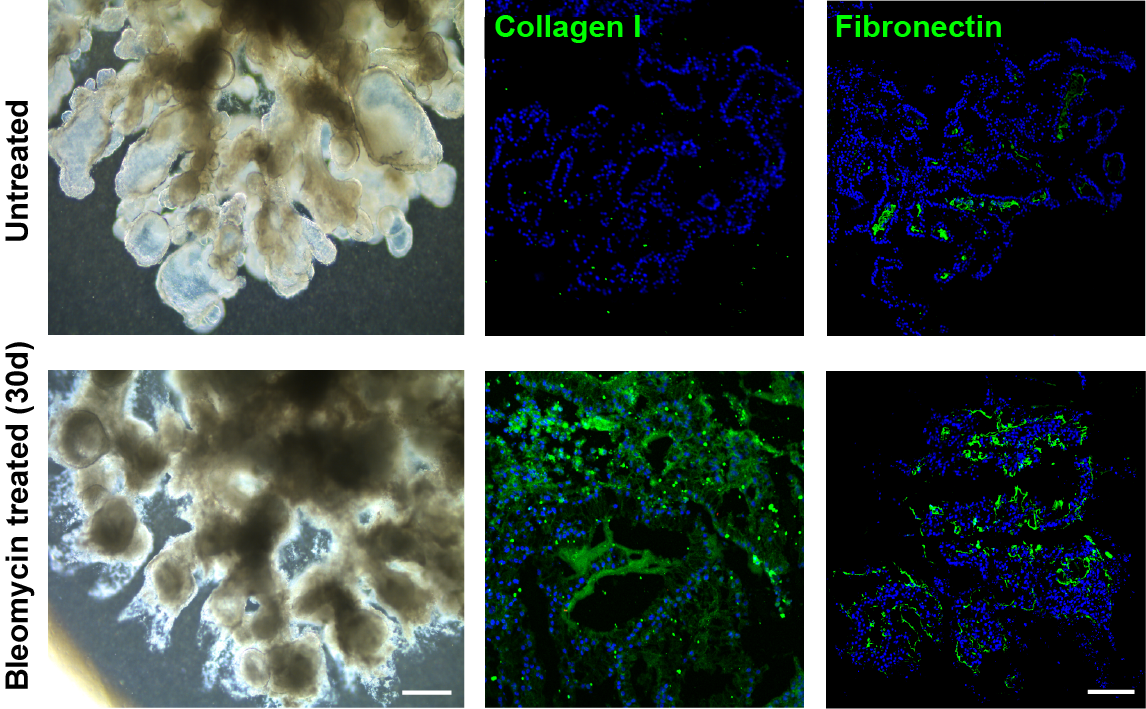
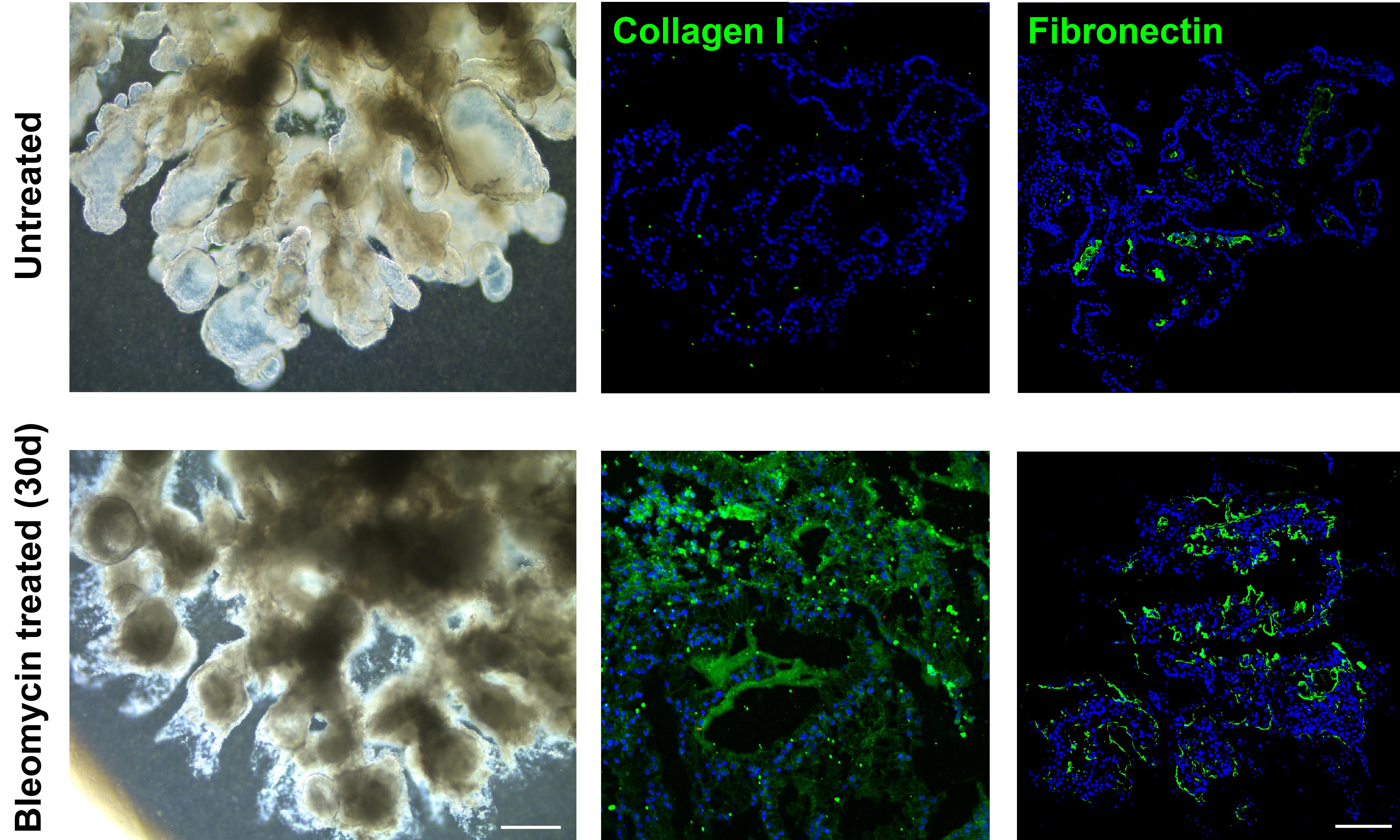
An iLung treated with 30-d bleomycin manifested increased dead cells, reduced bronchi/alveoli space, and collapsed architecture. Scale bar = 200 μm.
Compared with control that treated with PBS only, 30-d bleomycin induction resulted in significant ECM accumulation in iLung, identified by the increased staining area of Collagen I and Fibronectin with immunofluorescence. Scale bar = 200 μm.
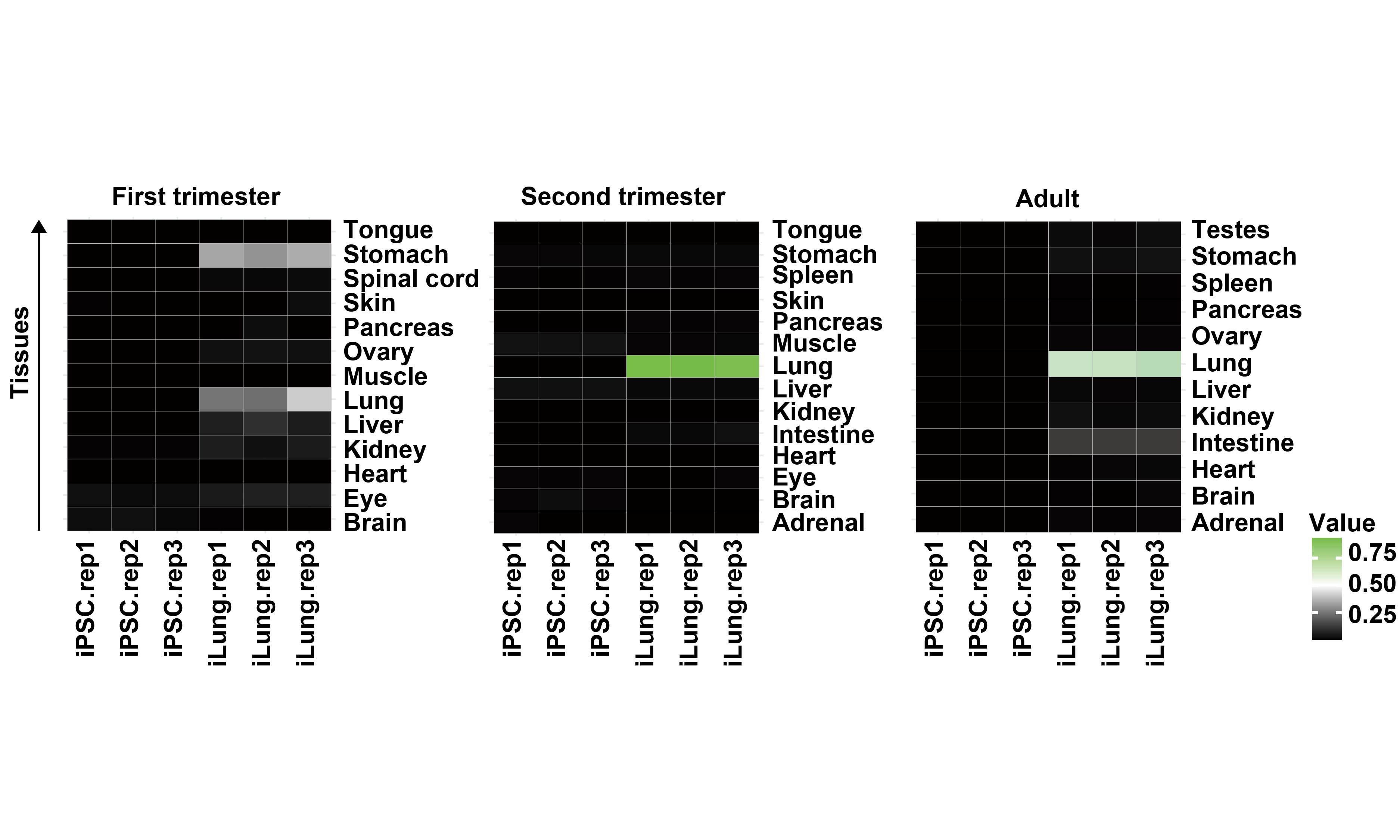
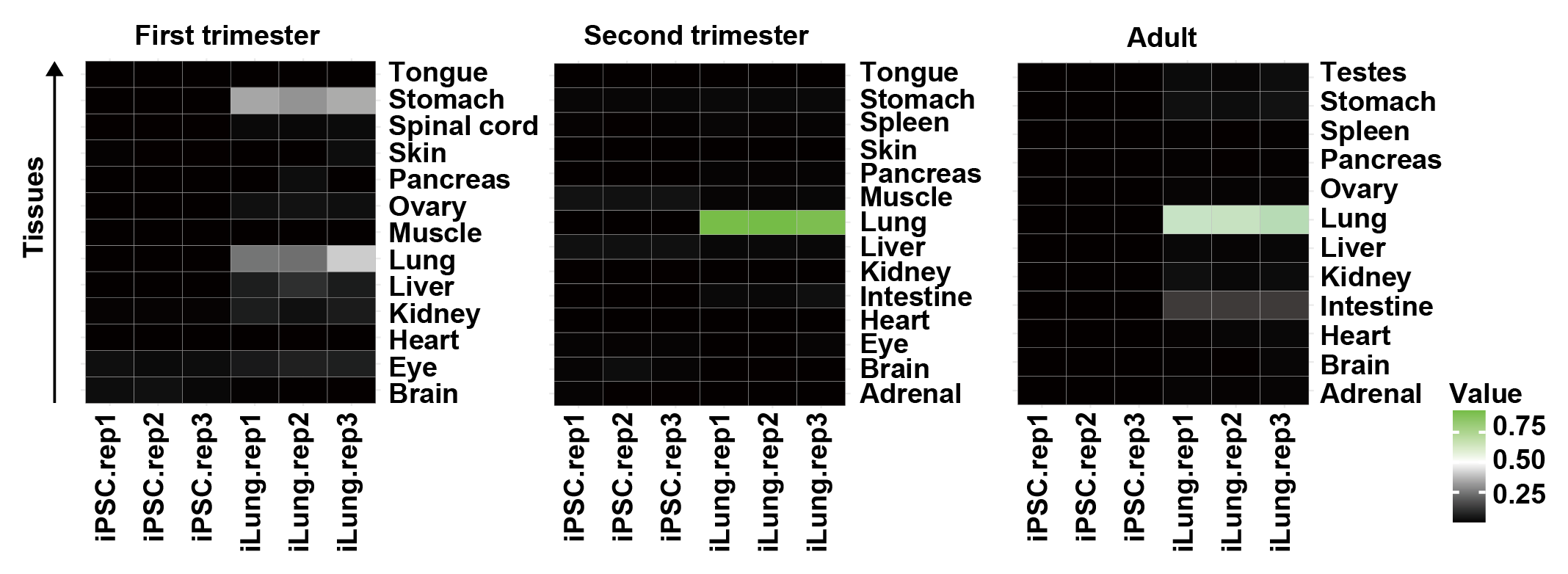
Assigning Developmental Stages to iLung with KeyGenes Tool
Liu W, Zhao Y, Fan J, et al. Smoke and Spike: Benzo [a] pyrene Enhances SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection by Boosting NR4A2‐Induced ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Expression[J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(26): 2300834.
Hein R F C, Conchola A S, Fine A S, et al. Stable iPSC-derived NKX2-1+ lung bud tip progenitor organoids give rise to airway and alveolar cell types[J]. Development, 2022, 149(20): dev200693.
Han Y, Duan X, Yang L, et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors using lung and colonic organoids[J]. Nature, 2021, 589(7841): 270-275.
Strikoudis A, Cieślak A, Loffredo L, et al. Modeling of fibrotic lung disease using 3D organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Cell reports, 2019, 27(12): 3709-3723. e5.
Porotto M, Ferren M, Chen Y W, et al. Authentic modeling of human respiratory virus infection in human pluripotent stem cell-derived lung organoids[J]. MBio, 2019, 10(3): 10.1128/mbio. 00723-19.